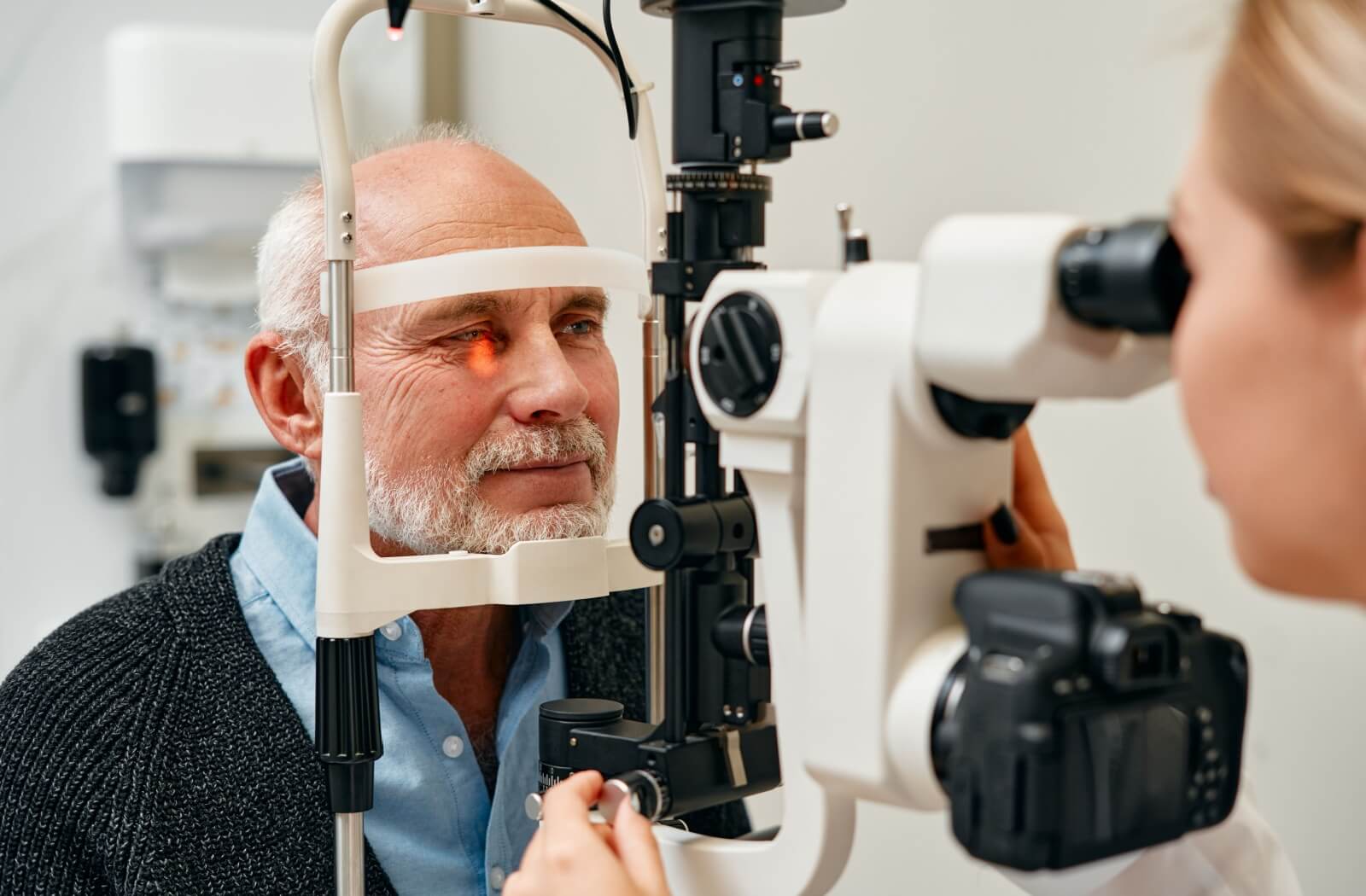
Living with diabetes can often feel like you’re juggling too many balls at once, especially when it comes to managing its impact on your daily life. Among the myriad concerns, eye health stands out as particularly crucial.
For many diabetics, maintaining sharp vision is not only about seeing clearly but also about securing independence and quality of life. Generally, vision loss from diabetic eye problems can’t be reversed, but proper treatment can protect your eyes and potentially even reverse the disease’s progression.
Diabetes & Its Impact On Vision
Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts how your body manages blood sugar (glucose) levels. Glucose is crucial for your health since it serves as a primary energy source for the cells that compose your muscles and tissues. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters your bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps glucose enter your cells to be used for energy.
However, if you have diabetes, this process doesn’t work properly, leading to elevated glucose levels in the blood. Over time, having too much glucose in your bloodstream can result in a variety of health issues, such as nerve damage, kidney problems, and complications affecting your eyes, including diabetic retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss.
Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication is crucial in mitigating these risks.
Types of Diabetic Eye Problems
Diabetes can increase your risk of several eye problems, each with its challenges. Some of these conditions are more treatable than others, but understanding them is the first step toward effective management. They include:
- Diabetic retinopathy: This is the most common condition related to diabetes and occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to blood vessels in the retina. These damaged vessels can leak or bleed, leading to vision problems.
- Diabetic macular edema (DME): While technically a complication of diabetic retinopathy, DME can be treated separately. It involves swelling in an area of the retina called the macula, which is responsible for clear central vision.
- Cataracts: People with diabetes are much more likely to develop cataracts, which occur when the eye’s lens becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision.
- Glaucoma: This group of eye conditions damages the optic nerve, vital for good vision, and can lead to vision loss if untreated. Diabetics may be up to twice as likely to develop glaucoma.
Other Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy
While diabetes is a primary contributor to diabetic retinopathy, several other factors can increase the risk of developing this eye condition. Here are some common risk factors:
- How long you’ve had diabetes
- Poor blood sugar management
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Pregnancy
- Tobacco use
Reversing Diabetic Eye Problems
When it comes to reversing eye problems related to diabetes, there is a glimmer of hope, especially if the conditions are diagnosed early.
You may be able to effectively manage diabetic retinopathy in its early stages through improved blood sugar control and lifestyle changes, which may prevent further damage and even stabilize vision.
Medical interventions such as laser treatments or surgeries may help preserve vision but typically do not fully restore it to normal. A procedure called a vitrectomy could be used to remove blood and scar tissue from the eye. While you may experience clearer vision afterwards, it’s important to talk to your eye doctor about the benefits and risks.
For diabetic macular edema, treatments like anti-VEGF injections or corticosteroids can reduce swelling and improve vision in many patients; however, they often need to be ongoing to maintain results.
Cataracts, unlike retinopathy and DME, can be treated by surgically removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial one, which often restores vision to an excellent state.
Glaucoma, however, is more challenging. While damage from glaucoma is usually irreversible, managing intraocular pressure with medications, laser treatments, or surgery can prevent further vision loss.
Managing Your Diabetes
Methods for managing diabetes typically depend on the type, but it’s crucial for reducing the risk of eye complications and other health issues. Here are some practical steps that can help:
- Regular monitoring: Keep track of your blood sugar levels by checking them as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Healthy diet: Opt for a balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins, while limiting sugary and processed foods. It comes down to knowing how foods affect your blood sugar.
- Physical activity: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Medication adherence: Take prescribed medications consistently and as directed by your doctor to manage blood glucose effectively.
- Routine Eye Exams: Schedule regular appointments to help detect any signs of diabetic eye conditions early.
Your Eyes Deserve the Best Care
Understanding diabetic eye problems is empowering. Armed with knowledge, you can take proactive steps to manage your eye health. Remember, while some conditions may not be fully reversible, their progression can often be halted, preserving your vision and enhancing your quality of life.
Insight Eyecare offers comprehensive eye exams and personalized care plans tailored to your needs. Book an appointment today and join a community dedicated to supporting your eye health journey.
Let’s keep your vision clear and vibrant, together.